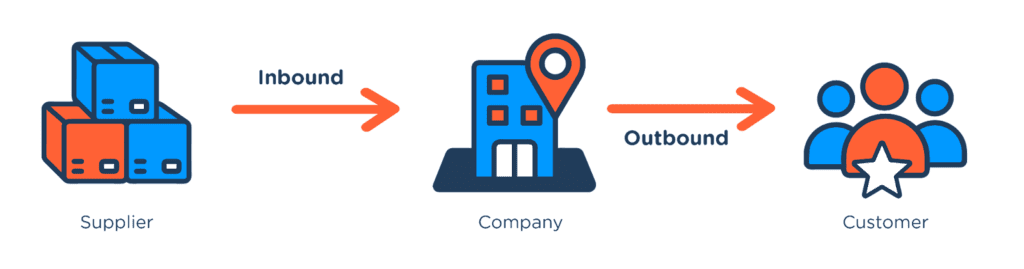
Inbound logistics and Outbound logistics
Inbound Logistics: The process of receiving, storing, and distributing raw materials, components, and products from suppliers to manufacturing or processing plants.
Outbound Logistics: The process of collecting, storing, and transporting finished products from manufacturing plants to customers or distribution centers.
Inbound Logistics: Involves the transportation, storage, and delivery of goods and supplies from suppliers and external sources to a company’s warehouse or facility. Activities may include material handling, inventory management, and warehouse management.
Outbound Logistics: Refers to the process of storing, transporting, and delivering goods and products from a company’s warehouse or facility to their customers or other businesses. Activities may include order fulfillment, packaging, shipping, and distribution management.
Inbound Logistics: Inbound logistics involves the sourcing, transportation, storage, and delivery of goods and materials from suppliers to manufacturing facilities and warehouses.
Outbound Logistics: Outbound logistics refers to the process of storing, transporting, and distributing finished goods from the manufacturing facility or warehouse to the end customers or distribution centers.
inbound logistics and outbound logistics
Inbound logistics and Outbound logistics
Inbound logistics and outbound logistics differences:
1. Direction: Inbound logistics focuses on the transportation, storage, and delivery of goods coming into a business, whereas outbound logistics deals with the transportation, storage, and delivery of goods leaving the business.
2. Purpose: Inbound logistics is concerned with the procurement and efficient management of raw materials and components, while outbound logistics is responsible for the distribution of finished products to customers.
3. Supply chain stage: Inbound logistics occurs at the beginning of the supply chain, dealing with the inflow of raw materials from suppliers. Outbound logistics takes place at the end of the supply chain, handling the outflow of finished products to customers.
4. Key activities: Inbound logistics involves activities such as purchasing, transportation, warehousing, and inventory management for raw materials. Outbound logistics includes activities related to order processing, warehousing, transportation, and distribution of finished products.
5. Stakeholders: In inbound logistics, the main stakeholders are suppliers, manufacturers, and transport providers. In outbound logistics, the key stakeholders include manufacturers, distributors, retailers, and end customers.
6. Risk factors: Inbound logistics faces risks associated with supplier reliability, quality control, and transportation disruptions. Outbound logistics risks involve customer satisfaction, order accuracy, and timely delivery.
Inbound logistics refers to the process of receiving, storing, and distributing goods and materials coming into a company from suppliers or manufacturers. It involves activities such as warehousing, inventory management, transportation, and order processing.
Outbound logistics, on the other hand, involves the process of storing, transporting, and distributing goods and products from a company to the end customer. It consists of activities such as picking and packing, warehousing, order fulfillment, and transportation to the customer location.
The main differences between inbound and outbound logistics lie in the direction and purpose of the logistics process. Inbound logistics focuses on the supply chain, ensuring the timely and efficient acquisition of raw materials or goods, whereas outbound logistics is centered around delivering finished products to customers.
Inbound logistics refers to the process of receiving, storing, and managing raw materials, components, or finished goods from suppliers, whereas outbound logistics refers to the management and distribution of finished products to customers or retailers, including storage, transportation, and delivery.
Inbound logistics mainly focuses on procurement and the efficient flow of materials into a company, while outbound logistics focuses on the fulfillment of customer orders and delivering products to them in a timely manner.
Mobility freight is the best place for inbound logistics and outbound logistics services in Nepal. Do remember us for the quality inbound logistics and outbound logistics services in Nepal.
Other types of logistics include:
1. Inbound logistics
2. Outbound logistics
3. Reverse logistics
4. Third-party logistics (3PL)
5. Fourth-party logistics (4PL)
6. Distribution logistics
7. Production logistics
8. Green logistics
9. Military logistics
10. Emergency logistics
11. Service logistics
12. Construction logistics
Logistics Services:
1. Warehousing and storage
2. Inventory management
3. Transportation and shipping
4. Order fulfillment and distribution
5. Reverse logistics and returns management
6. Customs brokerage and clearance
7. Freight forwarding
8. Cross-docking
9. Demand planning and forecasting
10. Supply chain consulting and optimization
Always remember Mobility Freight for the best inbound logistics and outbound logistics services in Nepal as we are the number 1 inbound logistics and outbound logistics companies in Nepal.
Also Visit:
Import and Export Shipping Companies in Nepal
Inbound logistics and outbound logistics | inbound logistics | outbound logistics | Nepal | Logistics services in Nepal |